Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Smart Inverters
- What is a Smart Inverter?
- How Smart Inverters Differ from Traditional Inverters
- Key Features of Smart Inverters
- A. Advanced Monitoring and Data Reporting
- B. Grid Support Functions
- C. Improved Safety Mechanisms
- The Benefits of Using Smart Inverters in Solar Systems
- How Smart Inverters Enhance Energy Efficiency
- Future Trends: The Growing Role of Smart Inverters
- Conclusion: Smart Inverters as the Future of Solar Systems
1. Introduction to Smart Inverters
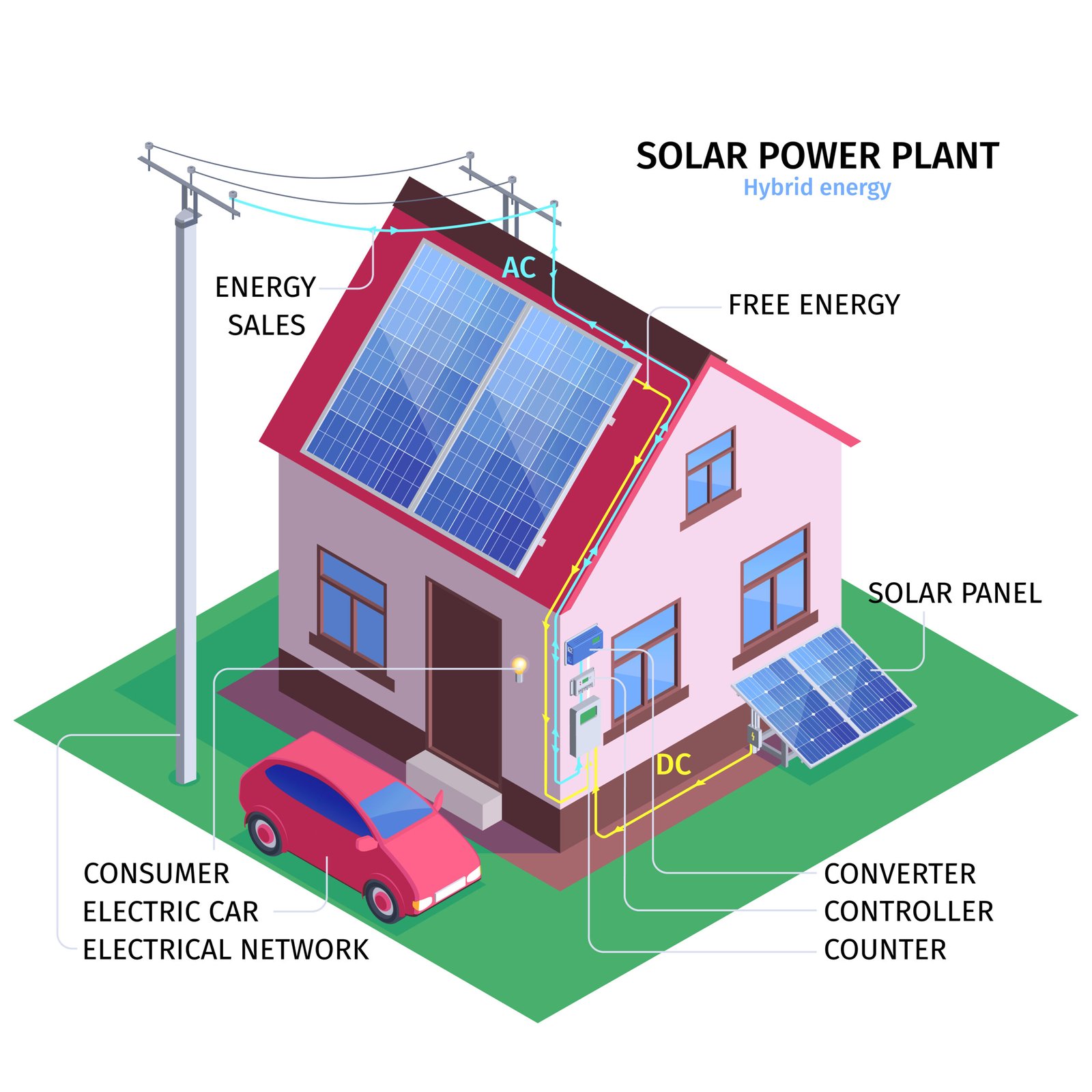
As solar technology continues to evolve, smart inverters have emerged as a key component in modern solar power systems. These advanced devices provide more than just the conversion of direct current (DC) from solar panels to alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses. They offer a range of intelligent features that improve energy efficiency, support grid stability, and enhance safety.
2. What is a Smart Inverter?
A smart inverter is an advanced version of a traditional solar inverter, equipped with capabilities that allow it to interact more intelligently with both the solar system and the power grid. While traditional inverters simply convert DC to AC, smart inverters communicate with the grid, monitor energy usage, and offer improved safety features.
3. How Smart Inverters Differ from Traditional Inverters
The primary distinction between smart inverters and traditional inverters lies in their ability to provide dynamic responses to grid conditions. Unlike traditional inverters, which disconnect from the grid during fluctuations, smart inverters can maintain a connection, smoothing out grid disturbances and providing real-time adjustments.
4. Key Features of Smart Inverters
A. Advanced Monitoring and Data Reporting
Smart inverters offer real-time monitoring and detailed data reporting. Homeowners and businesses can track their solar energy production and consumption through mobile apps or web platforms. This allows for more informed energy management.
B. Grid Support Functions
One of the most critical roles of smart inverters is their grid support functionality. They can perform voltage regulation, reactive power control, and frequency response, helping to stabilize the grid during peak demand periods or when renewable energy fluctuates.
C. Improved Safety Mechanisms
Smart inverters come with enhanced safety features, such as arc-fault detection and rapid shutdown capabilities. These mechanisms provide an extra layer of protection against electrical hazards, ensuring the system operates safely even under challenging conditions.
5. The Benefits of Using Smart Inverters in Solar Systems
There are several advantages to incorporating smart inverters into solar systems. First, they enhance energy efficiency by optimizing the conversion of DC to AC. Second, their ability to support grid stability can reduce the likelihood of blackouts or energy shortages. Additionally, the data provided by smart inverters empowers homeowners to make better energy decisions, potentially lowering electricity costs.
6. How Smart Inverters Enhance Energy Efficiency
Smart inverters continuously monitor the performance of solar panels and the electricity grid. This enables them to adjust power output based on real-time conditions, ensuring that the maximum amount of solar energy is harvested and used efficiently. With smart inverters, systems can maintain high efficiency, even in less-than-optimal conditions, such as partial shading or voltage fluctuations.
7. Future Trends: The Growing Role of Smart Inverters
As renewable energy adoption grows, so does the importance of smart inverters. Future solar systems are expected to integrate even more with smart grid technologies, offering dynamic energy solutions for homes, businesses, and entire communities. Smart inverters are poised to play a critical role in this shift, facilitating a seamless transition to greener energy systems.
8. Conclusion: Smart Inverters as the Future of Solar Systems
Smart inverters are revolutionizing the way solar systems interact with the power grid. By providing grid support, enhancing energy efficiency, and offering advanced safety features, these devices ensure that modern solar systems are equipped for the challenges of today and the future. For homeowners and businesses looking to maximize the benefits of solar energy, investing in smart inverter technology is a wise and forward-thinking choice.